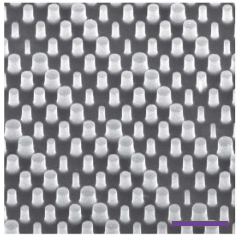
The Pancharatnam-Berry or geometric phase is widely used for making metalenses and metasurfaces. It allows for broadband performance and relatively straightforward design. In particular dielectric rectangular structures are widely used.
One disadvantage of these anisotropic structures is that they require a circularly polarized incident light. Recently some papers have shown that a polarization insensitive metalens can be made even with polarization sensitive structures.
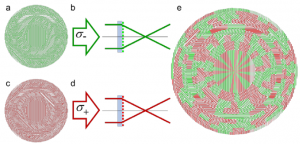
The picture on the left shows the work of Lin et al. who interleaved two circularly polarizing metalens designs (red and green). One for left and one for right circular polarized light, the result is a polarization insensitive lens. The drawback of this approach is that the focussing efficiency decreases since each polarization state effectively “sees“ only half a lens. Read the full paper here:
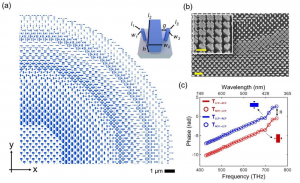
The rightpicture shows an alternative approach. Chen and colleagues use only two orientations of nano-fins: 0 and 90 degrees. These two orientations cause respecitvely a 0 and 180 degree phase shift for both left and right circular polarized light. By this choice the resulting metalens is automatically polarization insensitive. This elegant approach effectively means that only a binary hologram can be made to reproduce the desired phase profile. The entire paper is in the link below: